Tracking Marketing KPIs dives deep into the world of key performance indicators, shedding light on their significance and impact on business success. From understanding the basics to interpreting data for strategic decisions, this topic is a must-know for any marketing enthusiast.
Setting the right KPIs, tracking them effectively, and making sense of the data are all key components in optimizing marketing strategies for maximum impact. Let’s explore the ins and outs of Tracking Marketing KPIs in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding Marketing KPIs
![]()
Marketing KPIs, or Key Performance Indicators, are essential metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and strategies. They help businesses track their performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions to achieve their goals.
Importance of Marketing KPIs
Marketing KPIs provide valuable insights into the success of marketing efforts and help businesses measure their return on investment. By focusing on specific KPIs, companies can align their marketing activities with their overall objectives and drive growth.
- Conversion Rate: This KPI measures the percentage of website visitors who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC helps businesses understand how much it costs to acquire a new customer, allowing them to optimize their marketing spend.
- Return on Investment (ROI): ROI calculates the revenue generated from marketing activities compared to the cost, indicating the effectiveness of campaigns.
Differences from Other Metrics
Marketing KPIs are distinct from other types of metrics as they are specific to marketing goals and objectives. Unlike general performance metrics, KPIs are directly tied to business outcomes and provide actionable insights for improvement.
- Website Traffic: While website traffic is a valuable metric, it does not necessarily indicate the success of marketing campaigns in driving conversions or revenue.
- Social Media Followers: The number of social media followers may not directly correlate with business success, making it less relevant as a KPI compared to metrics like engagement rate or lead generation.
Common Marketing KPIs
Marketing KPIs can vary depending on the industry and business objectives, but some common ones include:
| KPI | Description |
|---|---|
| Click-Through Rate (CTR) | Measures the percentage of people who click on a specific link or ad. |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) | Determines the total value a customer brings to a business over their entire relationship. |
| Email Open Rate | Indicates the percentage of recipients who open an email campaign. |
Setting Relevant KPIs: Tracking Marketing KPIs
In order to track the success of marketing efforts effectively, businesses must set relevant Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with their specific goals and objectives. This process involves careful consideration and strategic planning to ensure that the chosen KPIs provide meaningful insights into the performance of marketing campaigns.
Criteria for Selecting Meaningful KPIs
When selecting KPIs, businesses should consider the following criteria to ensure that they are relevant and align with their business goals:
- Relevance: KPIs should directly measure progress towards specific marketing objectives, such as increasing brand awareness or driving website traffic.
- Measurability: KPIs should be quantifiable and easily measurable to track progress over time accurately.
- Achievability: KPIs should be realistic and achievable based on the resources and capabilities of the business.
- Timeliness: KPIs should provide timely insights to allow for adjustments to marketing strategies as needed.
Customizing KPIs Based on Unique Objectives
Businesses often customize KPIs based on their unique objectives to ensure that they are measuring the right metrics for their specific needs. For example:
- A business focused on increasing online sales may prioritize KPIs related to website conversions, average order value, and customer acquisition cost.
- A brand looking to improve customer engagement may track KPIs such as social media interactions, email open rates, and customer satisfaction scores.
- A company aiming to enhance brand visibility might measure KPIs like search engine rankings, social media followers, and media mentions.
Tracking KPIs Effectively
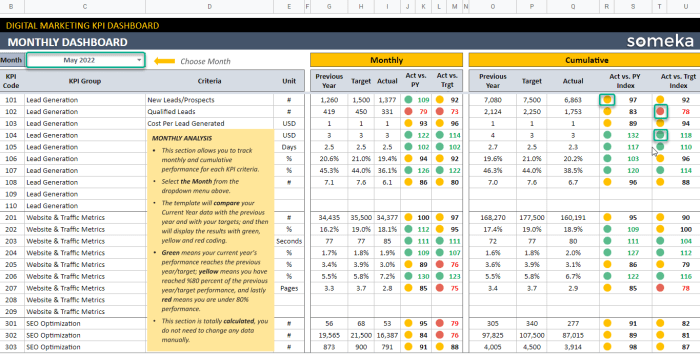
In the world of marketing, tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) is crucial for evaluating the success of your campaigns and strategies. By effectively monitoring these metrics, you can make informed decisions and optimize your marketing efforts for better results.
Methods and Tools for Tracking Marketing KPIs
- Utilizing Analytics Platforms: Tools like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, and HubSpot provide detailed insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates.
- CRM Systems: Customer Relationship Management systems help track customer interactions, sales data, and campaign effectiveness.
- Social Media Insights: Platforms like Facebook Insights, Twitter Analytics, and LinkedIn Analytics offer data on engagement, reach, and audience demographics.
Importance of Real-Time Tracking versus Periodic Tracking
Real-time tracking allows marketers to respond quickly to changing trends and adjust strategies on the fly. Periodic tracking, on the other hand, provides a comprehensive overview of long-term performance trends and helps in making strategic decisions.
Tips for Ensuring Accurate and Reliable KPI Tracking
- Define Clear Objectives: Set specific goals for each KPI to ensure accurate measurement and evaluation.
- Use Consistent Data Sources: Ensure data consistency across all tracking tools and platforms to avoid discrepancies.
- Regularly Monitor and Analyze: Stay vigilant in tracking KPIs regularly to identify any deviations or anomalies in performance.
- Implement Data Validation: Verify the accuracy of data inputs and outputs to maintain the reliability of tracking results.
Interpreting KPI Data
To make the most of your Key Performance Indicator (KPI) data, it’s crucial to interpret it correctly. By understanding how to derive actionable insights from your KPI data, you can make informed decisions to drive your marketing strategy forward.
Significance of Benchmarking and Trend Analysis
Benchmarking and trend analysis play a vital role in interpreting KPI data as they provide context and comparison points for your performance metrics. By benchmarking your KPIs against industry standards or competitors, you can gain valuable insights into how well your marketing efforts are performing relative to others in the field. Trend analysis helps you identify patterns and fluctuations in your KPI data over time, enabling you to spot emerging trends and adjust your strategies accordingly.
- Utilize benchmarking to set realistic goals and track your progress towards achieving them.
- Regularly conduct trend analysis to identify long-term performance trends and make informed strategic decisions.
- Compare your KPI data with industry benchmarks to understand your competitive position and areas for improvement.
Examples of Leveraging KPI Data for Strategic Decisions, Tracking Marketing KPIs
Many businesses have successfully leveraged KPI data to drive strategic decisions and improve their marketing performance. For example, a retail company analyzing website traffic KPIs may discover that a particular product category is underperforming compared to others. By redirecting marketing efforts towards promoting this category, the company can boost sales and revenue.
“By analyzing our social media engagement KPIs, we identified the best-performing content types and tailored our content strategy accordingly, resulting in a significant increase in user interaction and brand awareness.”
- Use KPI data to identify areas of improvement and prioritize marketing initiatives based on performance metrics.
- Make data-driven decisions by interpreting KPI data in the context of your business goals and objectives.
- Continuously monitor and analyze KPI trends to stay agile and responsive to changes in the market environment.